Hydrologic cycle Diagram Quizlet

442 L. Wang-Erlandsson et al.: Interception and transpiration - Part 1: Temporal characteristics transpiration, vegetation interception, floor interception, soil moisture evaporation, and open-water evaporation depends on land use and meteorological conditions. For example, in-terception and soil moisture evaporation are ephemeral (Ger-
Water Cycle Mind Map
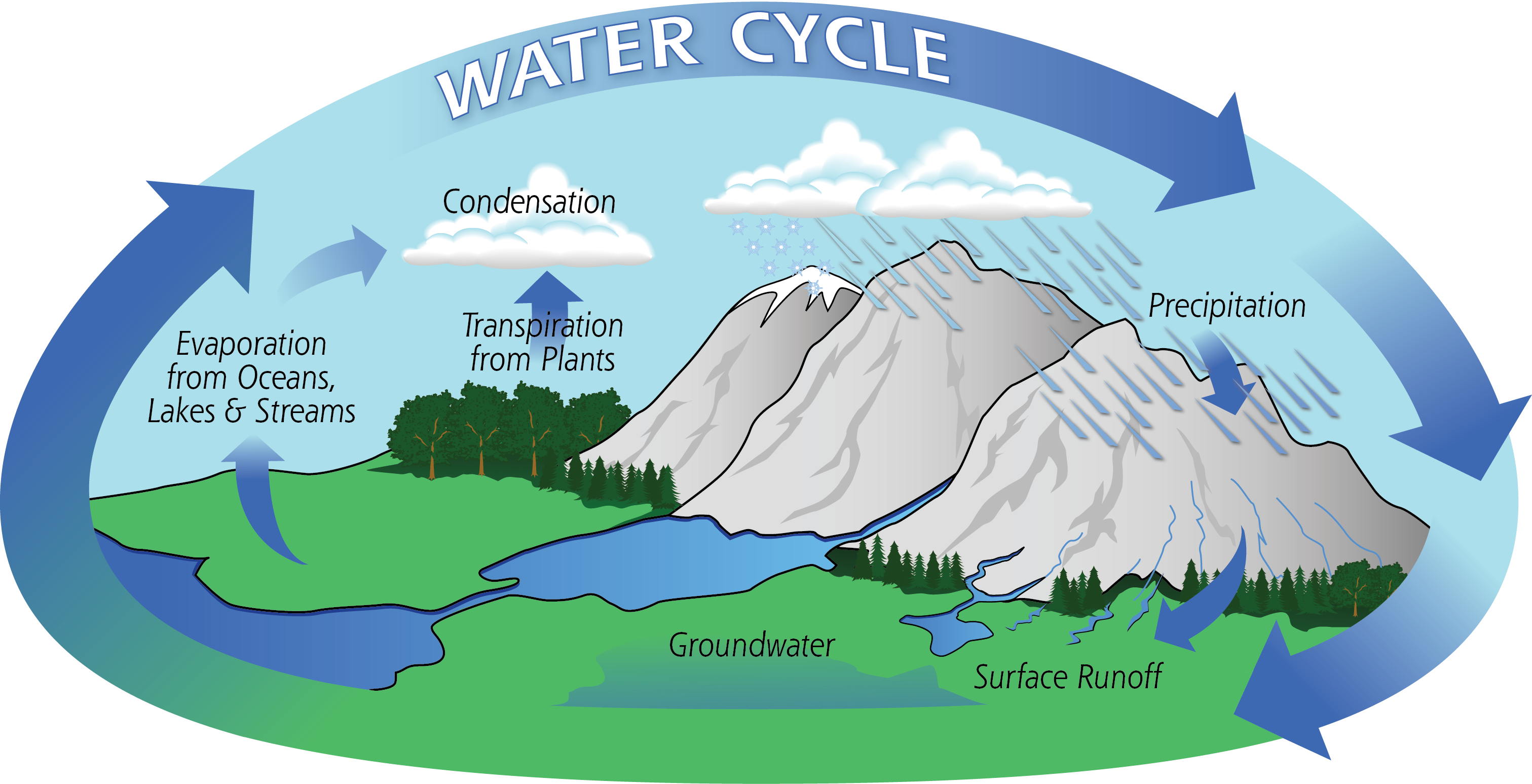
The water cycle is the endless process that connects all of that water. It joins Earth's oceans, land, and atmosphere. Earth's water cycle began about 3.8 billion years ago when rain fell on a cooling Earth, forming the oceans. The rain came from water vapor that escaped the magma in Earth's molten core into the atmosphere.
PPT Weather and Climate PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID690896
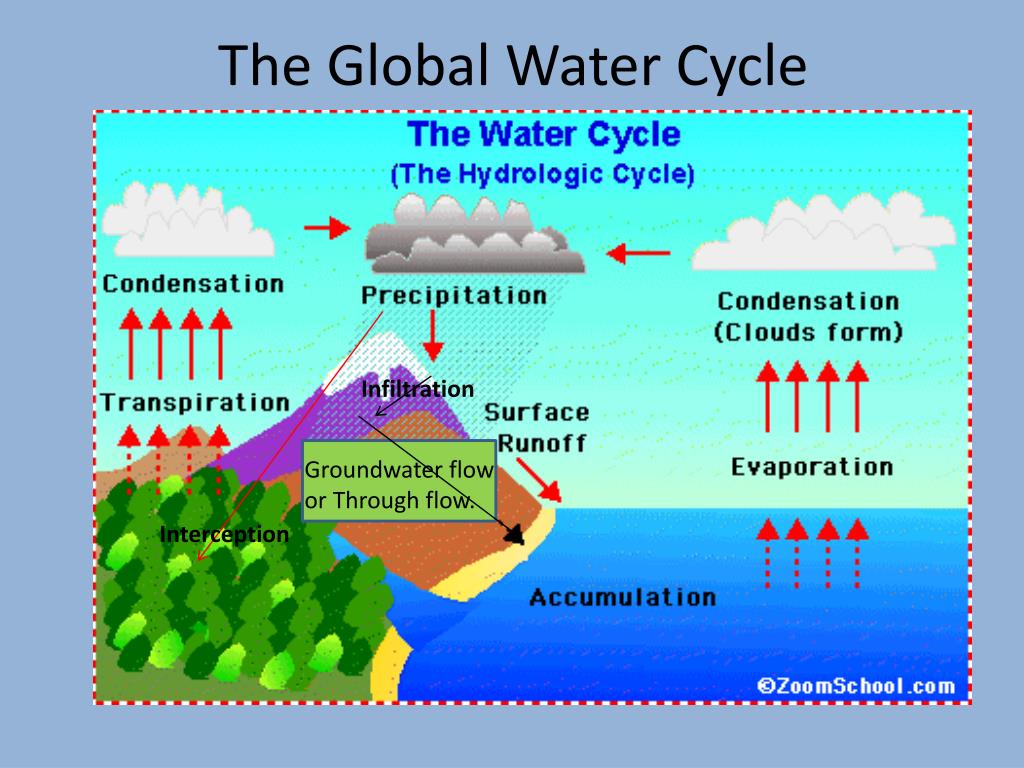
Interception [1] refers to precipitation that does not reach the soil, but is instead intercepted by the leaves, branches of plants and the forest floor. It occurs in the canopy (i.e. canopy interception ), and in the forest floor or litter layer (i.e. forest floor interception [2] ). Because of evaporation, interception of liquid water.
WATER CYCLE EVAPORATION TRANSPIRATION CONDENSATION PRECIPITATION INFILTRATION YouTube

The hydrologic cycle, or water cycle, is the cycling of water through the earth system. Not only is the hydrologic cycle a cycle of water, it is a cycle of energy as well. Over the next several pages we'll trace water as it passes through the earth system and the energy that accompanies it. Figure 10.2.1 10.2. 1: The Hydrologic cycle.
water cycle infiltration (diagram).jpeg

5.4: The Water Cycle. Go to the NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) description of the water cycle and read it carefully. The elements of the groundwater cycle are: Use the NOAA site to write a definition for each term above. 5.4: The Water Cycle.
The hydrological Cycle notesychs
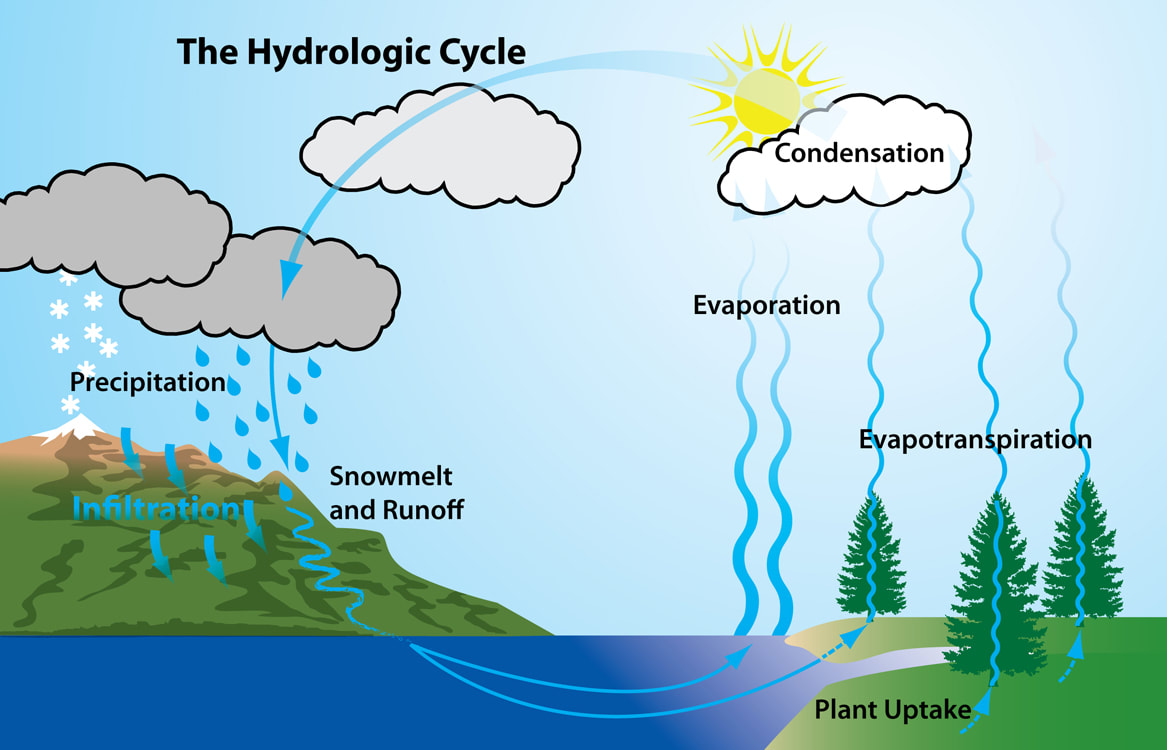
The water cycle describes how water is exchanged (cycled) through Earth's land, ocean, and atmosphere. Water always exists in all three phases, and in many forms—as lakes and rivers, glaciers and ice sheets, oceans and seas, underground aquifers, and vapor in the air and clouds. Evaporation, Condensation, and Precipitation. The water cycle consists of three major processes: evaporation.
What is the Hydrologic Cycle? (Video)
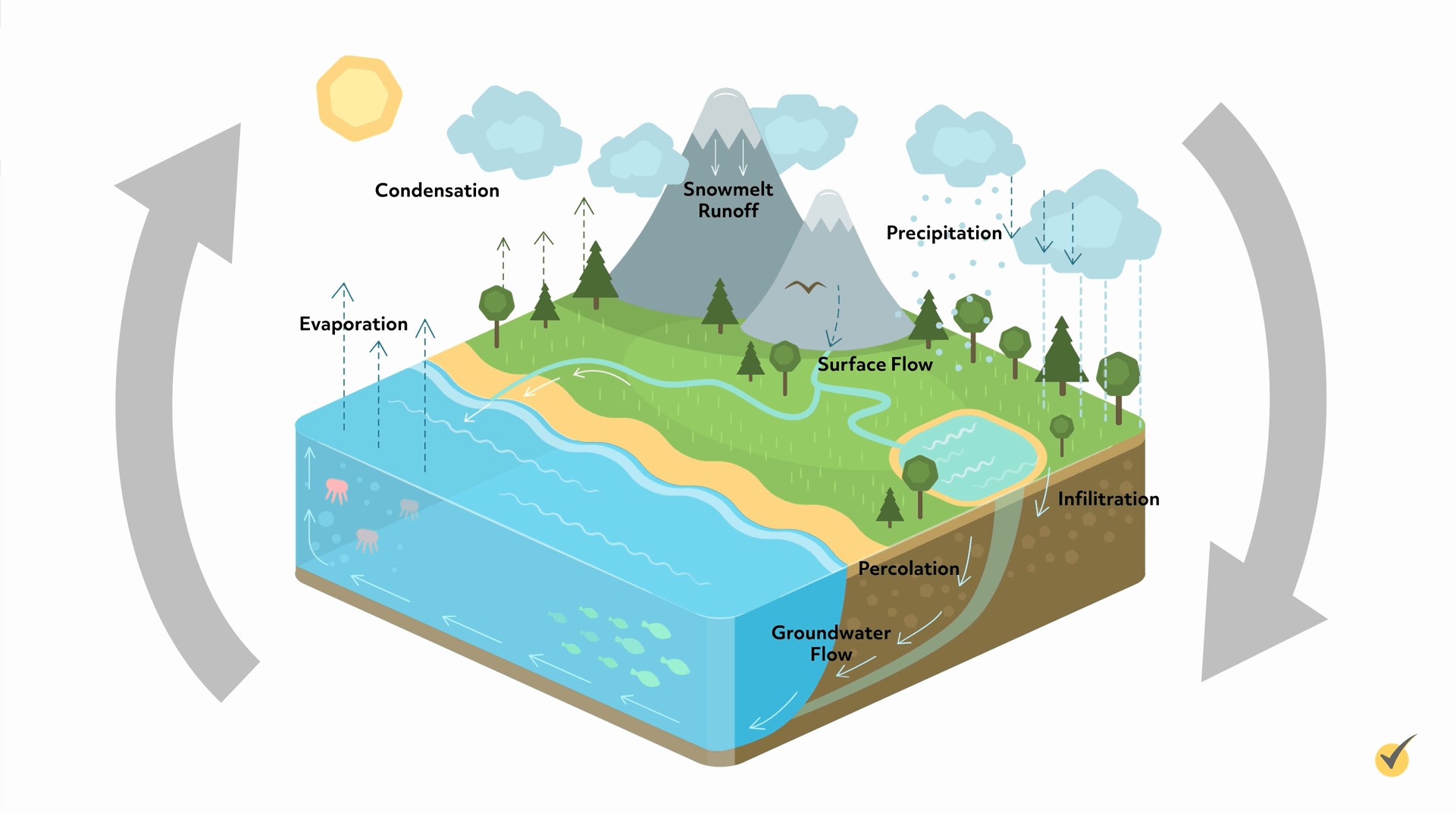
water cycle, cycle that involves the continuous circulation of water in the Earth - atmosphere system. Of the many processes involved in the water cycle, the most important are evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation, and runoff. Although the total amount of water within the cycle remains essentially constant, its distribution.
The Hydrologic Cycle

The water cycle is a fascinating process that involves the movement of water between different states and locations on Earth. In this article, you will learn how the water cycle works, what factors influence it, and how it affects weather and climate. This article is designed for middle school students who want to explore the science of Earth and space. Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization.
llustration of generalized hydrologic cycle for a hillslope showing... Download Scientific Diagram

THE WATER CYCLE. This is an education module about the movement of water on the planet Earth.. It can be studied by starting at any of the following processes: evaporation, condensation, precipitation, interception, infiltration, percolation, transpiration, runoff, and storage. The information presented below is a greatly simplified.
ALevel Resources River Processes Yorkshire Dales Rivers Trust

Environmental Science. Interception is the part of the rainfall that is intercepted by the earth's surface and which subsequently evaporates. In this definition the earth's surface includes everything that becomes wet after a rainfall event and that dries out soon after. It includes: vegetation, soil surface, litter, build-up surface, etc.
The Water Cycle (Hydrological Cycle) Diagram Quizlet

Canopy rainfall interception (Ei) is a key component of global water cycle. Here, the authors quantify Ei using flux tower data and machine learning, and find that rainfall gets less partitioned.
The Water Cycle Definition! Easy Science Lesson for Kids
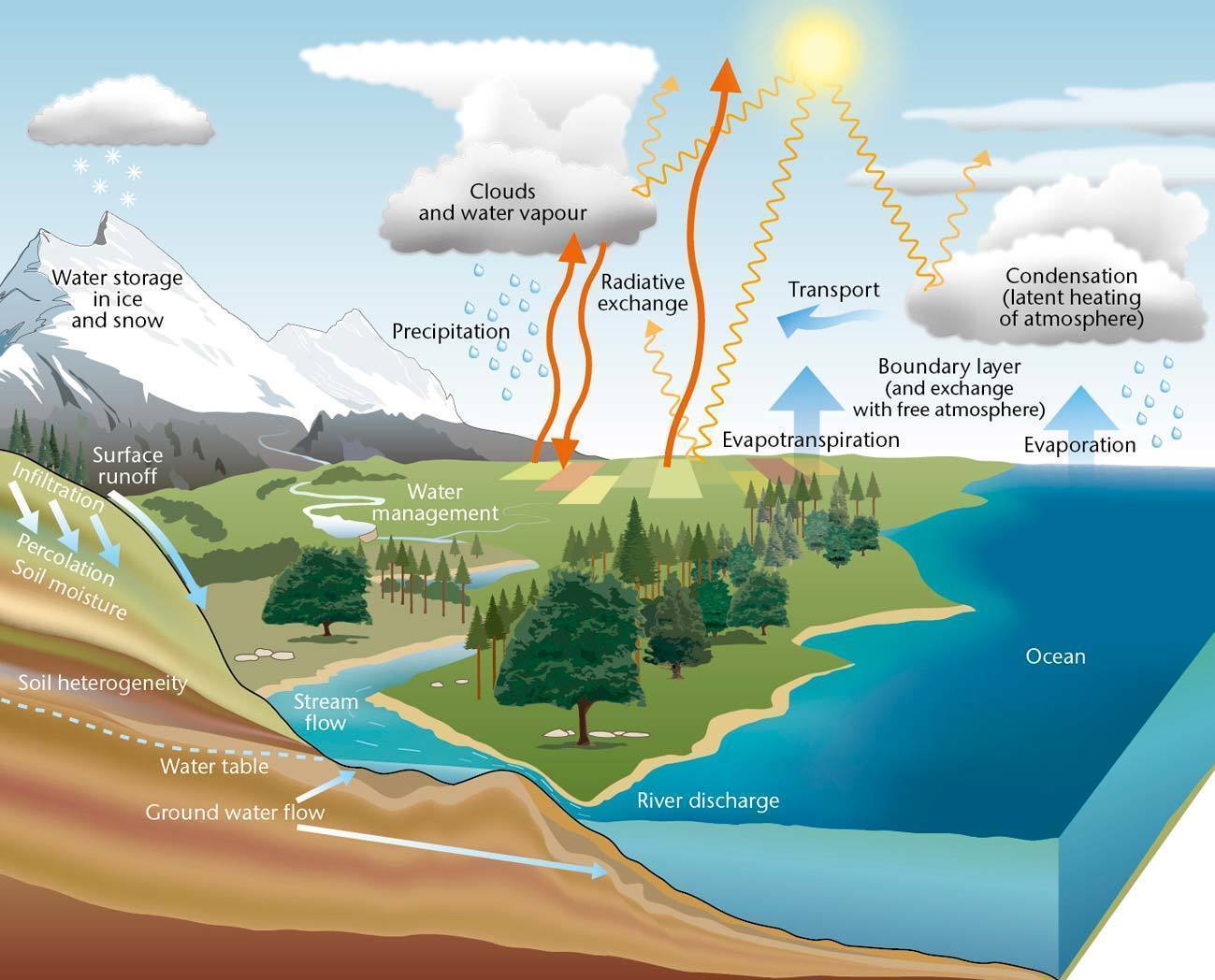
Interception. When precipitation reaches the surface in vegetated areas, a certain percentage of it is retained on or intercepted by the vegetation. Rainfall that is not intercepted is referred to as throughfall. Water that reaches the ground via the trunks and stems of the vegetation is called stemflow. The interception storage capacities of.
Water Cycle Transpiration Definition

We conclude that interception mainly works as an intensifier of the local hydrological cycle during wet spells and wet seasons. On the other hand, transpiration remains active during dry spells and dry seasons and is transported over much larger distances downwind, where it can act as a significant source of moisture.
The water cycle
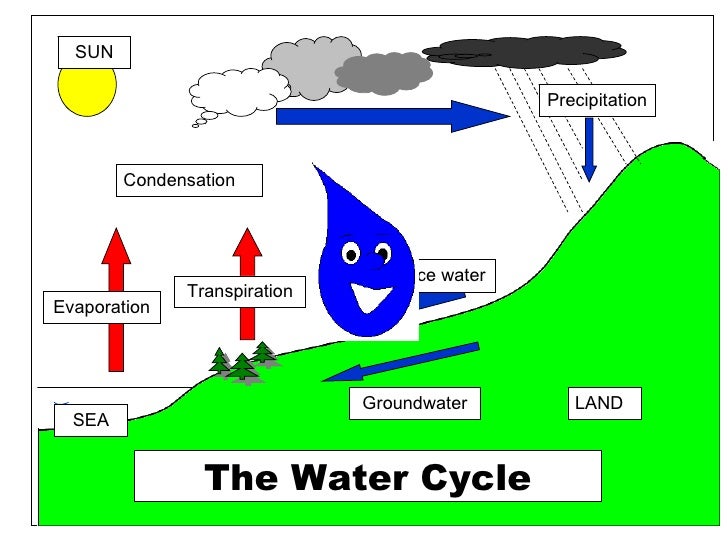
The water cycle. The water cycle, or hydrologic cycle, is driven by the Sun's energy. The sun warms the ocean surface and other surface water, causing liquid water to evaporate and ice to sublime—turn directly from a solid to a gas. These sun-driven processes move water into the atmosphere in the form of water vapor.
How the Earth's Water Cycle Works Owlcation

Interception. Interception is the temporary storage of water on the surface of plants and buildings before it reaches the surface. The rate of interception is determined by the time of year and the type of vegetation. Pine trees intercept more precipitation than oak trees. Buildings are designed to intercept rainfall through roofs.
Hydrologic Cycle the Recycling of Water A Learning Family
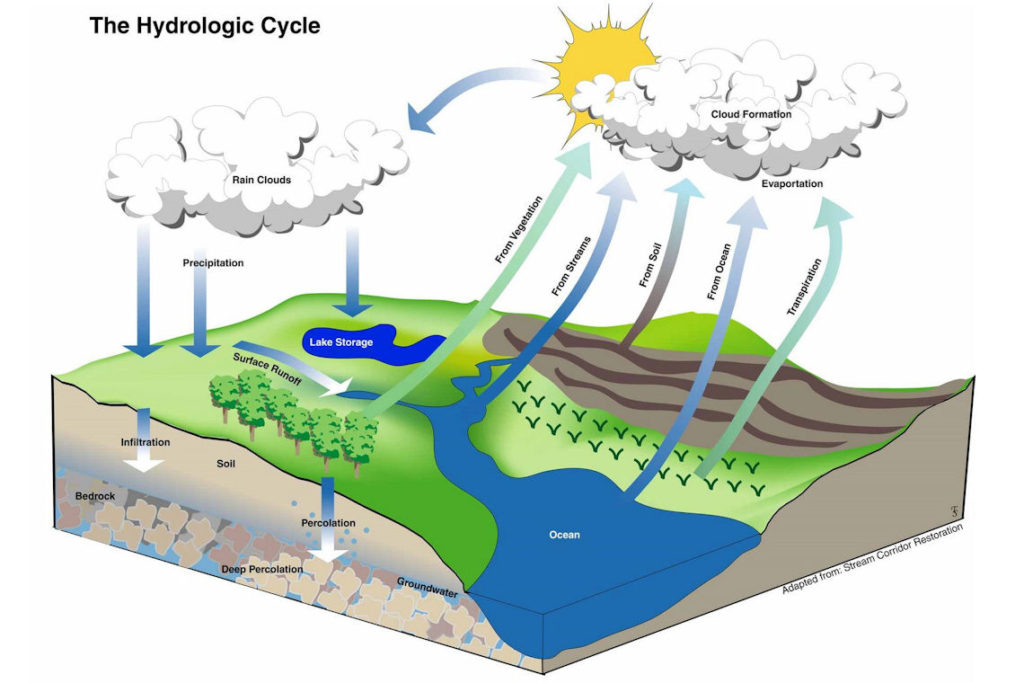
Interception is the part of the rainfall that is intercepted by the earth's surface and which subsequently evaporates. In this definition the earth's surface includes everything that becomes wet after a rainfall event and that dries out soon after. It includes: vegetation, soil surface, litter, build-up surface, etc. How much of the precipitation evaporates depends on land cover.
.

